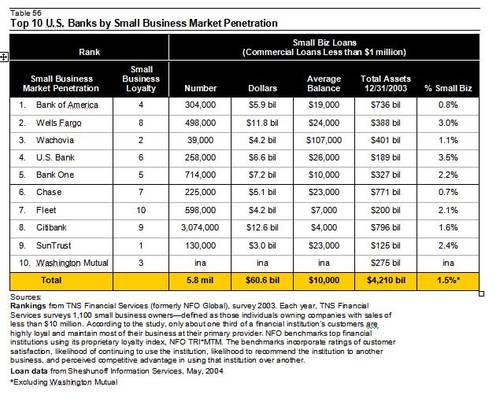
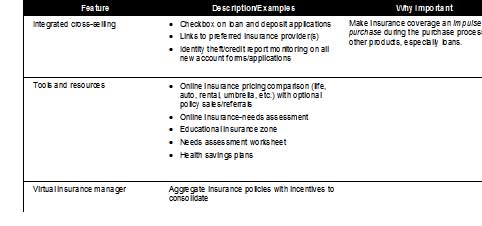
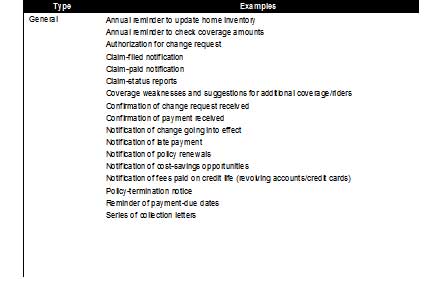
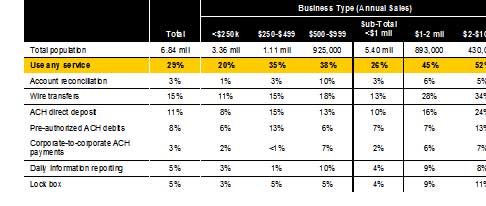
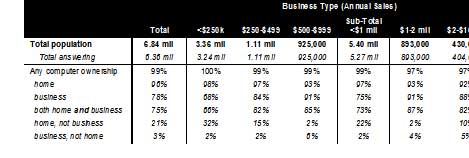
In the 2002 study of small business, TNS (formerly NFO Global Financial
Services) looked at which banks had the largest share of small businesses
relationships and which were ranked highest by small business clients.
SunTrust ranked highest in customer loyalty, followed by Wachovia
and Washington Mutual.
1. Bank of America
Pros:
· Three levels of business online banking: online banking with
bill pay, Business Connect for multi-users with varied levels of
access, and Bank of America Direct to manage all business finances
online.
· Good comparison chart of the three choices
· Resource center with informative articles on starting a
business and other topics
· Protect against online fraud link
Cons:
· Must scroll down to see all choices
· Hard-to-read small blue font for most links
· No separate URL or bookmark helper
2. Wells Fargo
Pros:
· Small business tab
· Excellent navigation and design, all viewable on a single
screen without needing to scroll.
· Clients can view personal and business accounts from a single
sign-on
· Single page, informative Small Business Newsletter
· Customers and non-customers can enter email address to signup
for newsletter
· Relevant and useful tips on product pages
· Product comparison pages as well as best product for your
business quiz
· Push a button to switch from English to Spanish and back again
· Link to Make this your first page at WellsFargo.com
Cons:
· No link to Security on the main page
· Not using liquid layout, so homepage appears small and
off-center at higher resolutions
3. Wachovia
Pros:
· Small business is one of the four main navigation
choices on the top
· Copy and headlines are solutions-oriented, e.g., Meeting
Your Needs, Resource Center
· Excellent navigation and layout on a single page
· Separate small business FAQs
· Relevant products and services packaged into “centers”:
Banking Center, Lending Center, Investing Center, Online Services Center,
Insurance Center, and HR Solutions Center
Cons:
· Must scroll to see information on bottom of screen
· No link to Security
4. U. S. Bank
Pros
· All major links are contained on a single page without
scrolling
· The no-frills style is easy to read
· Two solutions-oriented sections: Achieve Your Goals and
Small Business Center
· Separate Small Business login
· Link to Newsletter subscription
Cons
· Layout and design could be improved
· No link to Security
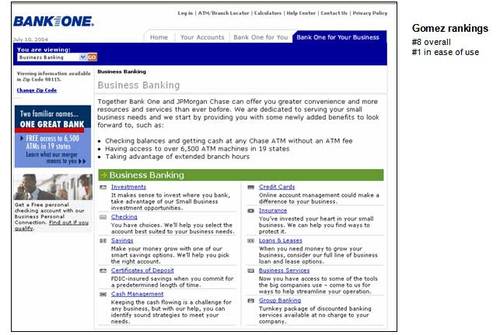
5. Bank One
Pros
· Product-oriented layout makes it easy to find specific products
· Small link to Security on bottom (not visible on
screenshot)
Cons
· There is no small business section, in fact the term is
not used in any header, although it is mentioned in the opening paragraph;
choices are Business Banking and Commercial, that defies
industry conventions and could cause lost business
· No solutions-oriented areas or resources section
· Copy is cliché-ridden and not benefits oriented;
for example under Insurance:
“You’ve invested your heart in your small business.
We can help you find ways to protect it.”
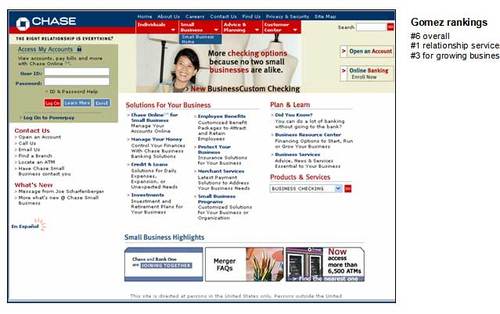
6. Chase
Pros
· Small business is one of the four primary navigation
choices on the top
· Excellent design and layout that fits on one page without
scrolling
· Solutions-oriented sections: Plan and Learn,
Solutions, and Business Stages
· Link on left to Have Chase Small Business contact you
· Privacy & Security link on top
· Prominent Open an Account and Online Banking: Enroll
Now boxes in upper right
· Liquid layout
Cons
· No quick navigation or separate URL for the small business
page, you have to click on the Small Business section on the home
page, then move your cursor down the cascading menu to the Small Business
Home, it only takes a few seconds but it’s still unnecessary extra
effort
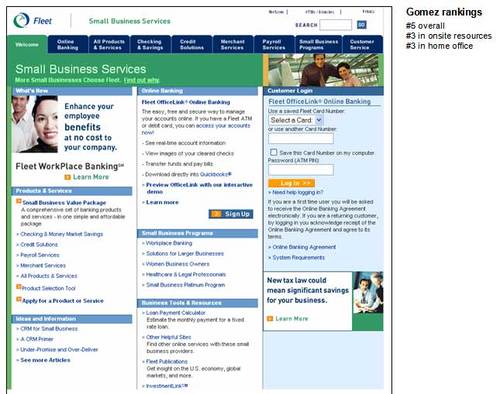
7. Fleet
Pros
· Separate URL
http://www.smallbiz.fleet.com/
· Tabs across the top help users find important subjects
· Link to Small Business Value Package (Note: Fleet also
offers a Small Business Platinum Program with a dedicated
relationship manager, faster funds availability, and priority phone service
· Solutions-oriented areas: Ideas and Information,
Business Tools & Resources
Cons
· Layout and design is a bit overwhelming
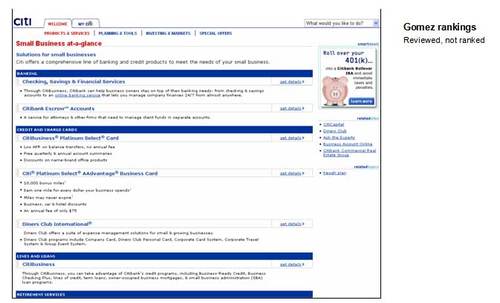
8. Citibank
Pros
· Using the drop-down menu you can navigate directly to relevant
business unit pages; the AAdvantage Business Card main page for
example is very well done
Cons
· Poor navigation off the home page: The only way to navigate to
the small business section is to use the drop-down menu on the right;
and because it doesn’t have a Go button, it took us 30 seconds before
we figured out you have to cursor down to Small Business at-a-glance
(screenshot above) in order to move to the small business section
· Poor navigation within the small business section: The four
main choices at the top of the page (Products, Planning, Investing,
and Special Offers) are NOT related to small business, they take you
back to consumer
http://www.citibank.com/ pages, and if you don’t use your back
button, you have to go through the full navigation routine to get back to
small business
· Must scroll down to see all the choices
· Main banking link (Checking, Savings, & Financial Services)
as well as the Online banking link cause a pop-up screen to load
which is dominated by an outdated self-promotion for online personal banking
with 2001 testimonial from Forbes magazine
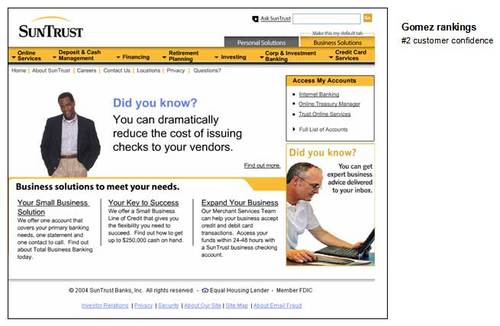
9. SunTrust
Pros
· Small Business Resource Center is a good area, although
it’s buried under the Online Services tab in the Business
Solutions area
· View only option for online banking, no money movement
allowed
· Ask SunTrust search box in upper right is handy, but it
doesn’t distinguish whether user in searching from business or personal
pages
Cons
· The top navigation bar is a mine field of cascading menus that
launch when the mouse travels over them, an out-of-date and annoying method
for primary navigation
· No dedicated Small Business homepage, other than the
Small Business Resource Center mentioned above and a mid-page link to
Your Small Business Solution which leads to a curious page entitled
Benefits that talks about Total Business Banking, but it’s not
clear if it’s geared to small businesses or not.
· Unclear and vastly different navigation/organization in the
various areas devoted to small business (e.g., Small Business Resource
Center)
10. Washington Mutual
Pros
· Link to content from StartupNation in upper-left corner; the
only bank in top 10 with headline targeting startups (see back page for more
information)
· Good online banking demo with audio highlights
· All the information shows on a single page without scrolling
· Liquid layout
Cons
· No link to Security
· Copy and headlines could be more solutions-oriented
· Layout is a bit sparse for a bank